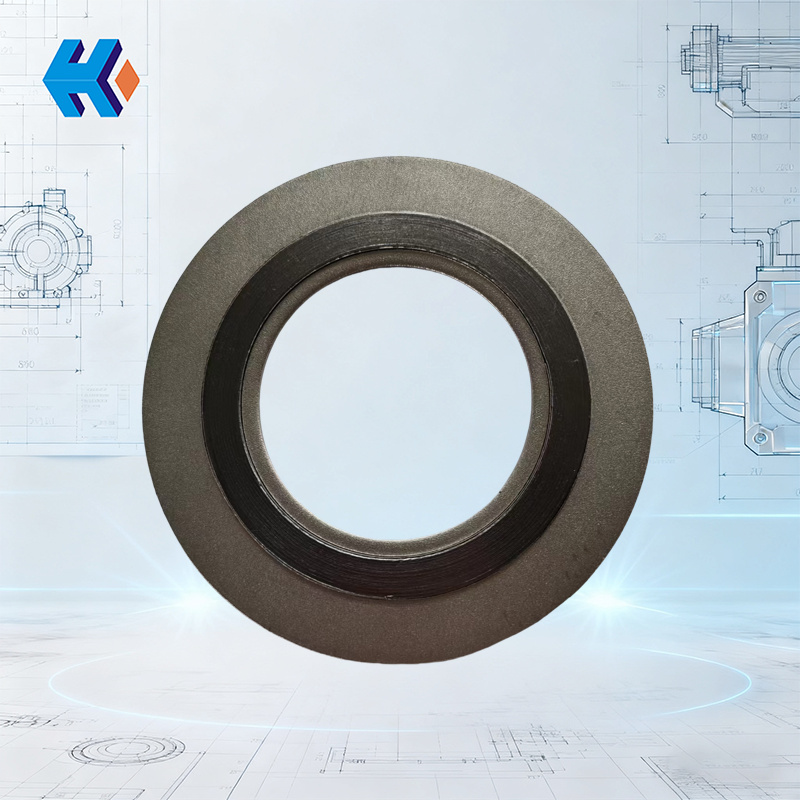
Inner and Outer Ring Metal Spiral Wound Gasket
Inner and outer ring metal spiral wound gaskets are sealing gaskets commonly used in harsh working conditions such as high temperature, high pressure, and strong corrosion. They are made by alternately winding a metal strip (such as carbon steel, stainless steel, nickel-based alloy, etc.) and a non-metallic filler strip (such as asbestos, graphite, PTFE, etc.), with metal rings (inner and outer rings) added on the inside and outside, forming a composite sealing structure. Their design combines the strength of metal with the sealing performance of non-metals, and they are widely used for flange connection sealing in equipment such as pipelines, valves, and pressure vessels in industries like chemical, petroleum, power, and metallurgy.
Structure and Function of Inner and Outer Ring Spiral Wound Gaskets
1. Winding Section: Consists of spirally wound metal and filler strips and is the core part of the seal:
- Metal Strip: Provides structural support and strength, ensuring the gasket does not easily deform under pressure. It also uses the elasticity of the metal to compensate for minor irregularities on the flange surface. Common materials include 304, 316 stainless steel (corrosion resistant) and Inconel 625 (for high temperature and pressure).
- Filler Strip: Provides sealing performance. It uses the plasticity of the non-metallic material to fill the gaps between the flange faces, preventing media leakage. Common materials include flexible graphite (good high-temperature and corrosion resistance), PTFE (chemical corrosion resistant, suitable for highly corrosive media), and asbestos (which has been gradually replaced by environmentally friendly materials).
2. Inner Ring:
Located on the inner side of the winding section, it is usually made of the same material as the metal winding strip. Its function is to increase the gasket's radial rigidity, prevent the winding section from deforming inward or "collapsing" under high pressure, and assist in positioning to ensure the gasket is accurately installed at the flange's center bore.
3. Outer Ring:
Located on the outer side of the winding section, it is often made of carbon steel or the same material as the metal strip. Its main functions are to limit the installation position of the gasket, prevent radial displacement between the flange faces, protect the edges of the winding section from damage, and provide support during installation, making it easier to place the gasket.
Main Features and Advantages of Inner and Outer Ring Spiral Wound Gaskets
-
Excellent Sealing Performance: The combination of the metal strip's elasticity and the filler strip's plasticity allows it to adapt to flange runout, misalignment, or thermal deformation. It maintains a good seal even with pressure and temperature fluctuations, with a leakage rate much lower than that of ordinary flat gaskets.
- Wide Application Range: It can withstand high temperatures (up to 1000°C or more, depending on the metal strip material), high pressures (up to 30 MPa or more), and various corrosive media (depending on the choice of filler and metal strip materials).
- Stable Structure: The reinforcement provided by the inner and outer rings makes the gasket resistant to damage from pressure or temperature changes, extending its service life and reducing maintenance frequency.
- Convenient Installation: The outer ring's positioning function simplifies the installation process. It ensures the gasket is centered without requiring precise alignment, reducing the impact of installation errors on the seal.
With the advantages of their composite structure, inner and outer ring spiral wound gaskets offer significant sealing reliability in harsh conditions. They are indispensable key sealing components in industrial equipment connections, and special attention must be paid to material compatibility during selection and installation to ensure the best sealing effect.